Fortinet got a lot right with its FortiGate product line and load balancing is no exception. They’ve made it easy for administrators with modest networks to easily accomplish network redundancy and load balancing. While load balancing can be used for various applications, its commonly used for load balancing between two ISPs and this is the subject we’ll be covering today.
The configuration detailed herein was completed on a FortiGate 100D with FortiOS 5.
Topology
The topology we’ll be using is pretty straightforward. A single FortiGate firewall separating an internal host from two load-balanced ISPs. Notably you likely won’t be assigned similar addressing by both your providers, this is merely for simplicity sake.
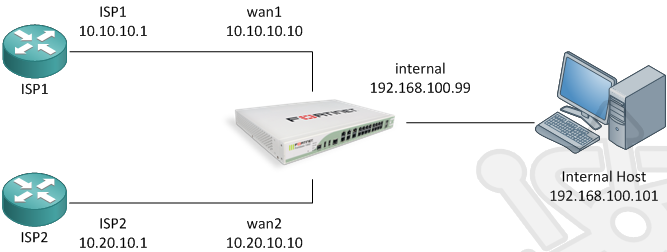
WAN
Our first stop will be to configure our wan interfaces. The FortiGate unit has two designated interfaces marked as wan1 and wan2 which we’ll use for connectivity to our ISPs. Let’s configure our first internet connection on wan1.
In the System pane, open the Network and then Interfaces menu items.
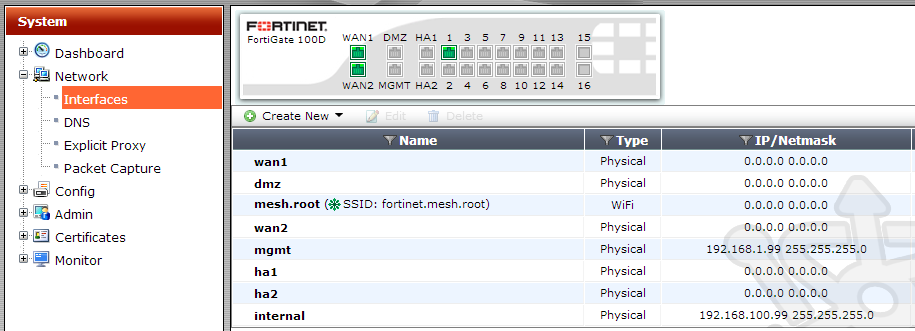
Inside the Interfaces dialog we’ll see the addressing assigned to each of the FortiGate’s interfaces. Let’s double-click on the wan1 interface to have a look at the settings.
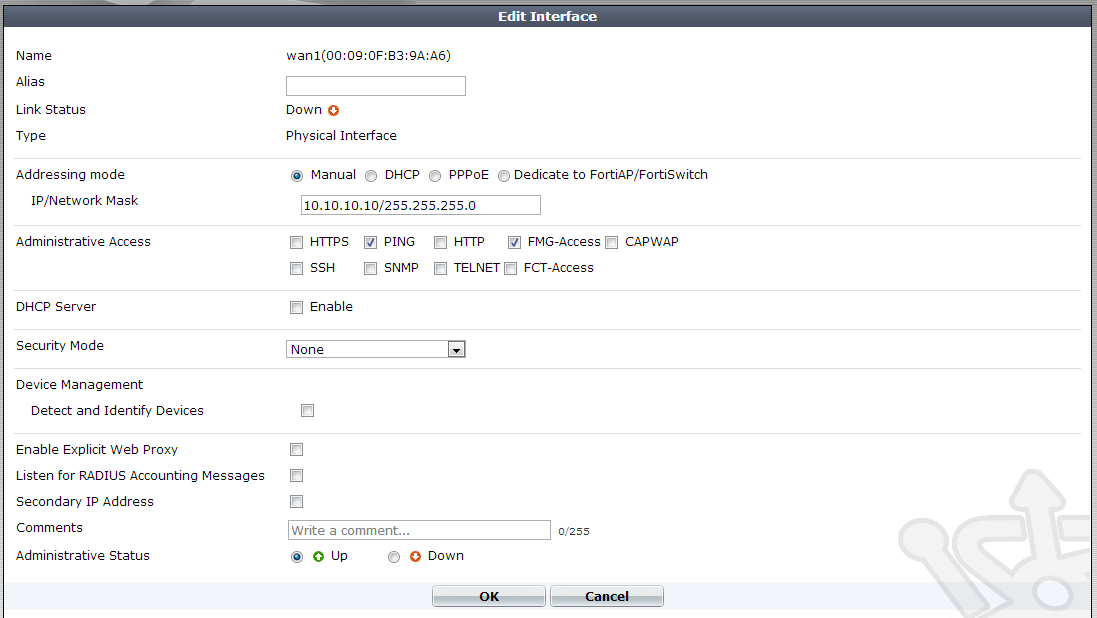
In the wan1 settings we’ll use the IP of 10.10.10.10 and network mask 255.255.255.0. You should be able to leave the rest as-is. Click OK.
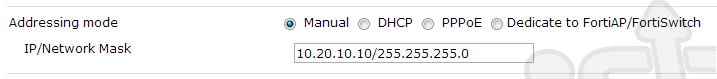
Now let’s do the same for the wan2 connection and this time with the address of 10.20.10.10.
Ensure your wan1 and wan2 interfaces are properly cabled into the appropriate internet connections. Once that’s done navigate to System, Dashboard where we can verify that the connections to our gateways are up and functioning.
Policies
With our wan interfaces online we need to have policies in place allowing the traffic to flow through them. In the left pane expand Policy and drill down into the Policy, Policy members. In here you’ll see the existing policies attached the device interfaces.
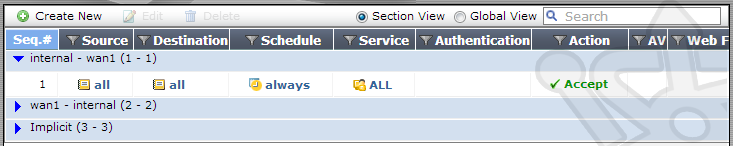
Expanding the internal – wan1 policy group you’ll see an existing policy. Double-click the existing rule.
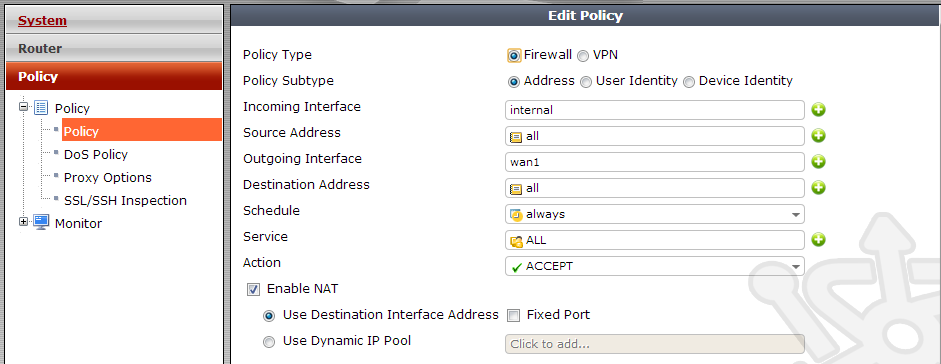
Opening the rule we see a definition allowing all internal traffic to NAT out the wan1 interface.
Close the rule. Now click Create New to define a new rule for our wan2 interface.
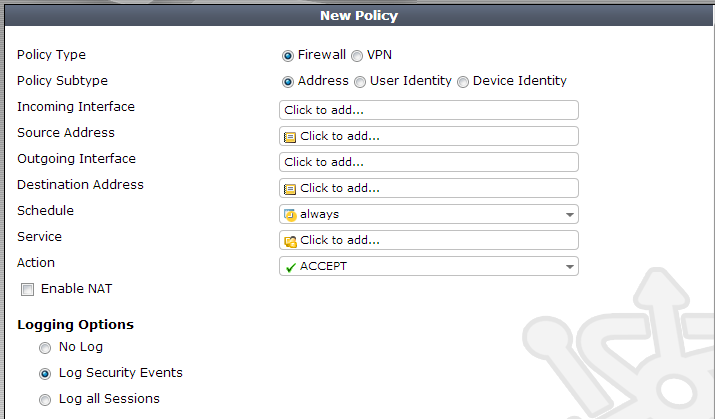
We’ll define the rule identical to the previous with the exception that the Outgoing interface will be wan2.
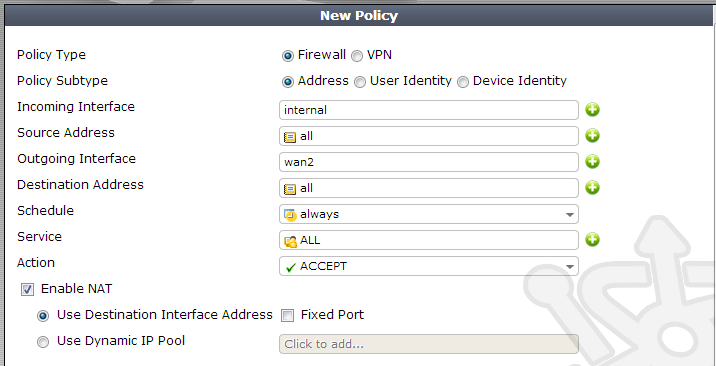
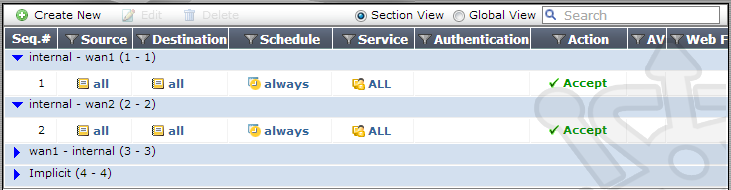
Save the settings and confirm that we have a policy for both internal-to-wan1 and internal-to-wan2.
ECMP Routing
Now that our interfaces and policies are in place, its time to turn our attention to load balancing. The load balancing in this case takes the form of Equal Cost Multi-Path routing (ECMP). ECMP is a routing methodology that allows multiple paths of the same cost to a single destination. We’ll be using ECMP to distribute traffic across two external interfaces, thereby balancing the load. FortiOS allows three different ways to configure ECMP:
- Source IP based – FortiOS balances the sessions based on the source IP.
- Weighted Load Balance – Traffic is load balanced between routes based on the weight assigned to each interface.
- Spillover – Traffic is distributed between ECMP routes based on the utilization of the interface.
There is one caveat when it comes to weighted and spillover load balancing on ForiOS involving cached routes. To explain this, let’s consider a timely example such as the Olympics. With a major event such as this, everyone is tuned in and more than a few employees are probably streaming a live video feed at their desk. Due to geography there’s a good chance that many of these users are hitting the same streaming node. When FortiOS creates a new session to a new destination IP, it creates a route cache. If another session is created from another source for the same destination IP, the FortiGate will use the existing route stored in the route cache. If our employees are watching the same stream, and assuming its coming from the same node, the traffic will ignore the rules of weighted or spillover routing and use the single interface.
Let’s now take a look at these three methods in more detail.
Source IP based
We’ll start from the top with Source IP based, which assigns wan interfaces based on the source IP. Once an internal host makes a connection across the wan interface, all subsequent sessions will traverse the same wan interface. This is the default ECMP method and the simplist.
Under the Router menu drill down into Static, Settings. Select Source IP based.
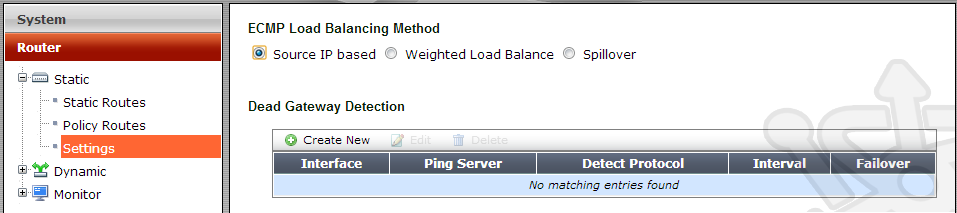
After choosing our ECMP method, we need to setup Dead Gateway Detection. This gives the FortiGate the ability to know when one of the routes is down.
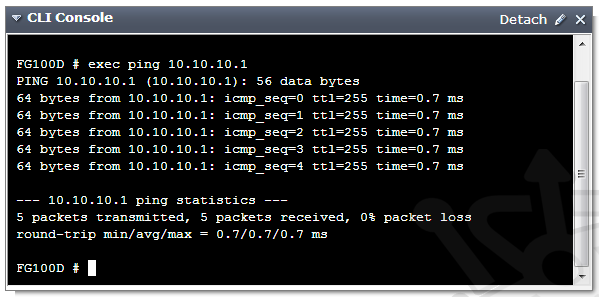
Under the Dead Gateway Detection section, click on Create New. For wan1 we’ll create an ICMP Ping detection against 10.10.10.1; effectively saying, if the next hop is down the route is considered unusable. We’ll set the Ping Interval and Failover Threshold to 5. This means that every 5 seconds the gateway will be checked, if the check fails 5 times the route will be treated as offline. In most cases you’d be using the next hop for verification of dead gateways, but there is nothing to say the ping server couldn’t be a remote server.
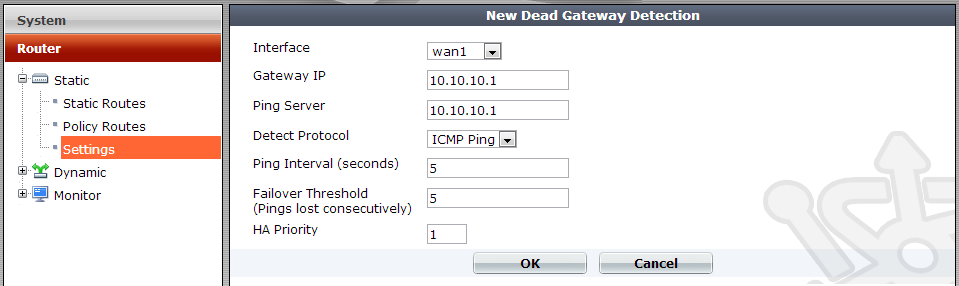
We then create a second dead gateway detector for our secondary external link.
Now that we have all the pieces in place, let’s take a look at load balancing in action. Navigate to Policy, Policy, Policy. Right click on the header and select Count from the drop-down menu.
In the policy view you’ll now see the packet count on each of the interfaces.
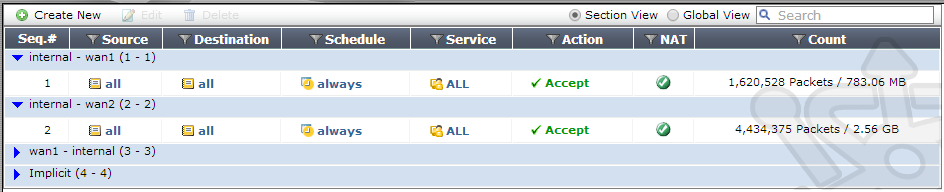
You should see the count on the wan1 and wan2 interfaces increasing. Your mileage my vary. As we chose source based routing, the amount of traffic on each wan connection will be dependent on the external interface assigned to each internal host.
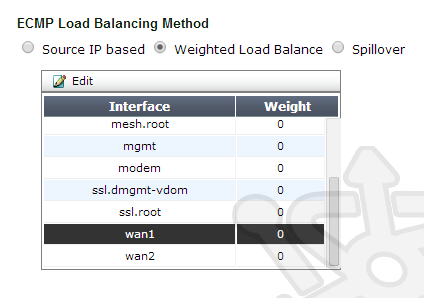
Weighted Load Balance
For the second option, Weighted Load Balance, FortiOS routes sessions taking into account the weight assigned to each interface. When a new session is created to a new destination (remember the earlier caveat), the FortiGate will generate a random number. Based upon the random number, weighted with the value assigned to the interfaces, one of the wan interfaces is chosen as the route for that session. This makes it so that a more heavily weighted interface is more likely to be chosen.
Navigate back to the Router menu, then down into Static and Settings. From here select Weighted Load Balancing. You will notice a new table that allows you to assign weights to each of the interfaces. When interfaces are given equal weight, then FortiOS will distribute traffic equally among those interfaces.
Spillover
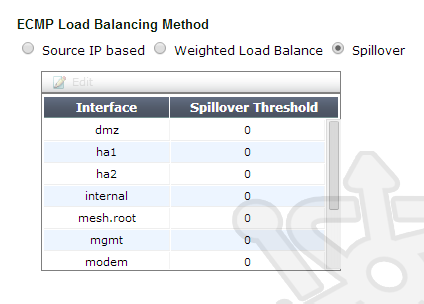
Finally when using Spillover and new session is created to a new destination, FortiOS will select the first interface where the utilization is lower than the specified limit. As the name suggests you can consider the analogy of containers with a finite capacity. Our first container will be filled until it reaches its capacity, any additional sessions will be spilled over to the next container until that container is filled, and so on. If the contents of first container drop below capacity, all new sessions will once again be poured into the first container.
When selecting the Spillover option, you will see a new table where you can populate desired thresholds. FortiOS accepts the range of 0-2097000 KBps for spillover thresholds. If the threshold on an interface is left at 0, no sessions will be sent to lower numbered interfaces.
This concludes the configuration of wan load balancing under FortiOS. Hopefully this has provided you enough background on the various Equal Cost Multi-Path routing options available to make an informed decision for load balacing your ISP connections.
hi, very good explanation. Can we use more than one option at same time?
Concerning ECMP, you can only pick a single load balancing
method per virtual domain. Organizations with multiple ISPs usually have one
higher performing connection, with a secondary in place as backup. In cases
such as this, Spillover is the obvious choice.
ok I see. Thanks !
But, how would be the network flow at the time when both ISP were running normally? I mean, once that is configured that way, should I need to create a route to use one of both ISP as default and the other one keeps as alternate one? Or, both are active-active and the fortigate chooses which one to use depending the utilization of each ISP?
With Dead Gateway Detection, the FortiGate will know the status of both WAN interfaces and whether they are accepting traffic. When both ISPs are running, the traffic will flow according to the ECMP method you’ve chosen (Source IP, Weighted or Spillover). As long as that’s configured appropriately then you just need to set the FortiGate’s internal address as your gateway. No need for you manage routes to the individual ISPs.
Hi Drew,
Thanks for the tutorial. I have a FortiGate 60D with v.5(build0929). Will i be able to configure WAN Load Balancing on it? I notice that my 60D does not have a Router menu. Thanks.
The “router” menu is no more présent in v5.
You can use System > Network > Routing in place of.
Exactly right. The GUI differs slightly depending on the model you’re using. If desired you should be able to access the standard GUI by issuing the following change:
Hi Drew,
Thanks for the tutorial. If we use proxy server for web browsing, i.e. only one source IP for interface traffic. And we would like to load share both internet link. What ECMP method should be used? Fortigate video demonstration use spillover with value 5 on both link, but no result is shown. Thanks.
I have made all the configurations, (it worked on a previous firewall too). But every time i connect a second Wan, the Wan 1 Goes Down. Does anybody had this problem before?